Constructivism learning theory is a philosophical theory that develops the logical and analytical abilities of the students based on their experience and their surrounding environment. The basis of this theory is that the real-life experiences of an individual play a significant role in their education process.
Constructivism learning theory stresses the fact that experiences are a prime source of knowledge in the life of the people. The founder of this theory is considered to be Jean Piaget.
MEANING AND DEFINITION OF CONSTRUCTIVISM
This theory of learning that states that an individual’s mental abilities and activities help in constructing their knowledge base. By analyzing our own rel0life experiences, we can make conclusions about the various happenings of the world. It is about building a perspective about things and constructing a meaning based on our experiences. Constructivism learning theory is highly influenced by the age and mental abilities of a person, and may not always be accurate. But as one progresses, it becomes more intricated and realistic.
Some of the chief driving elements or principles about constructivism theory of learning are:-
- Knowledge constructs through experiences it cannot be transferred.
- Having prior knowledge before joining a formal training, impacts the learning procedure.
- Knowledge is affected by our surroundings and the influences which may not be as per the global standards.
- For adequate knowledge, one needs to apply their efforts and actively participate in experience gaining activities.
CONSEQUENCES OF CONSTRUCTIVISM ON THE LEARNING PROCESS

In the teaching and education process, this theory can be a very profitable venture. In this practical approach can be adopted instead of textbook learning. Students are encouraged to utilize their thinking, reasoning and analytical skills. Education becomes more about concept application and establishing connections instead or taking in information.
For the teachers and educator, the teaching and instruction process becomes more centred towards the practical application of the concepts. The students learn from the hands-on approach of the things and interpret the results as per their perspective. It involves a lot of discussions and inquiry-based learning.
Assessment procedure also changes, as the teachers do not have to grade the students as per traditional assessments. Students themselves analyze their experiences, and so assessment is also involved as a learning process.
TYPES OF CONSTRUCTIVISM
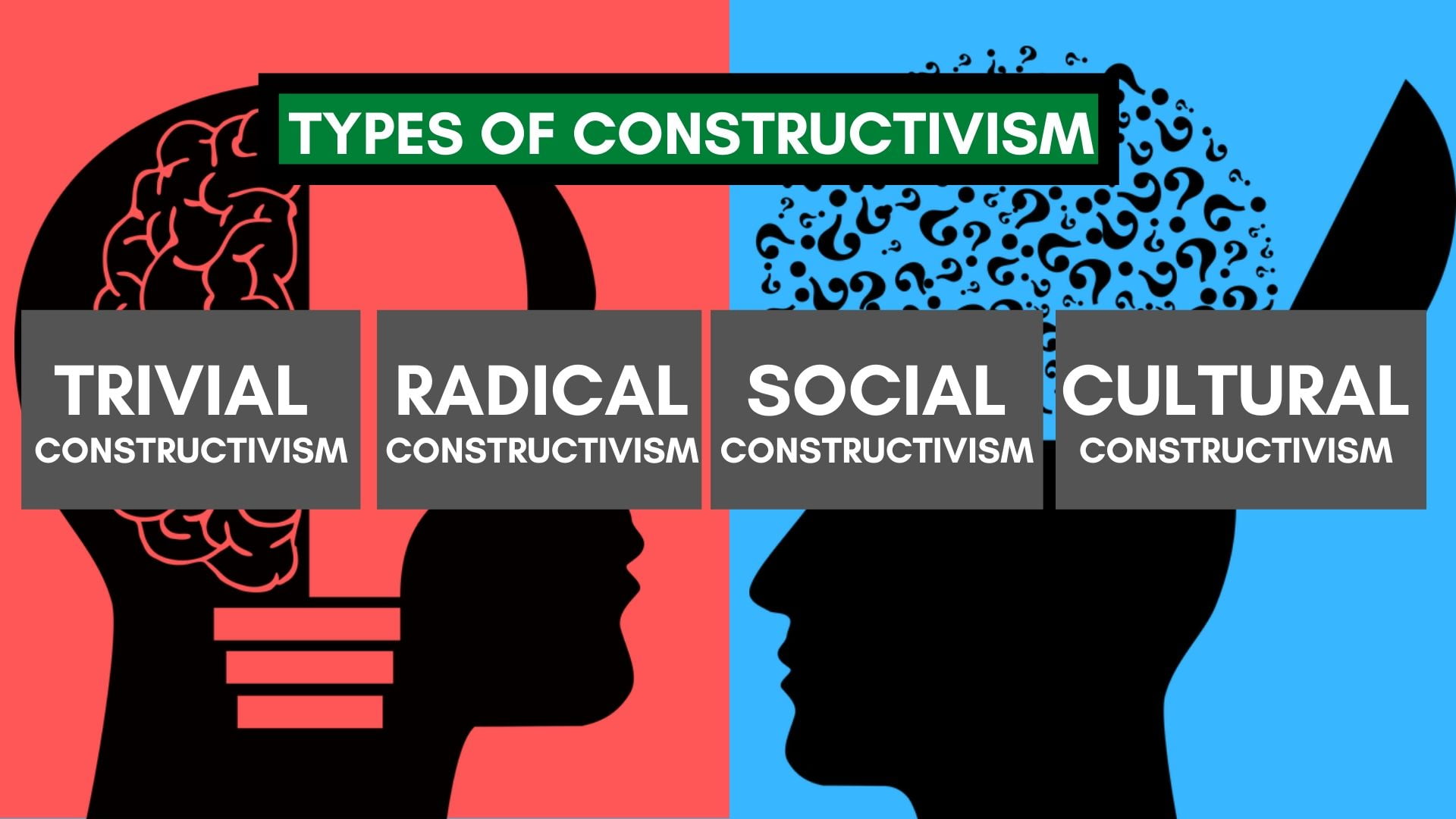
Generally, 4 significant types of constructivism are prevalent in the teaching world:-
- Inconsequential or Trivial Constructivism
- Social Constructivism
- Cultural Constructivism
- Profound or Radical Constructivism
A) TRIVIAL CONSTRUCTIVISM
It is one of the most basic and most straightforward amongst types of constructivism. It can be considered as the base of all the other theories. In this, knowledge is constructed by the learner through the interpretation of personal experiences based on his/ her cognitive and mental abilities. It is not just induced form the environment automatically and calls for active involvement.
B) RADICAL CONSTRUCTIVISM
Radical also emphasizes the construction of knowledge and states that textbook knowledge is not that meaningful. It can be connected to the working methodologies of mathematics, but it is difficult to understand and implement.
C) SOCIAL CONSTRUCTIVISM
Peers and people in society majorly influence the experience and learning process of an individual. Teachers family, friends, administrators and peers directly affect a student in various activities in a classroom. Even outside the school, this influence is significant. Hence, social constructivism is also an essential form.
D) CULTURAL CONSTRUCTIVISM
Culture and traditions of a place also affect a person’s perfective and opinion of things. By observing a person’s cultural background, one can make out the factors that affect their perception.
SOME COMMON BELIEFS OF CONSTRUCTIVISM
Here are some common beliefs and myths regarding constructivism learning thoery:
- Learning refers to the finding of meaning behind the concepts. Hence, it should be influenced by individuals daily life experiences and their surrounding atmosphere.
- Application-based learning is more important than bookish knowledge. Education should be imparted in context with practical learning and understanding the ideation behind the theoretical concepts.
- To ensure proficient and productive teaching practices, a teacher must be able to analyze the thinking capabilities of a student first. Their thinking procedures and assumptions should be taken into account.
- Instead of accessing and mugging up the answer to a problem, the student should be able to come to a conclusion about things from their point of view. This develops the involvement process of the students and also ensures a better understanding of the concepts involved in the teaching scenario.
- When a student joins an Indian school or any other type of formal training, he already has established a view about the world through this .
- A student can then evolve their perception based on the knowledge provided in the classroom and connect it with their experiences.
- New ideas can be constructed as a student has a good set of logical and reasoning skills. Also, concepts get relayed in a better manner through the practical learning approach, and they lead towards a better understanding.










Like!! I blog quite often and I genuinely thank you for your information. The article has truly peaked my interest.