In the vast and diverse country of India, where the contrasts between wealth and poverty are starkly visible, the root causes of poverty are many and multifaceted. Among these, the lack of education stands out as a critical factor that not only perpetuates poverty but also hinders the country’s progress towards economic stability and social equity. This article delves into how the absence of education directly contributes to poverty, exploring the barriers to education in India and proposing strategies to overcome these challenges.
The Direct Impact of Lack of Education on Poverty

Education is widely recognized as a fundamental right and a cornerstone of development. It empowers individuals with knowledge, skills, and the confidence to seek better employment opportunities, thereby increasing their income levels and contributing to economic growth. However, in India, a significant portion of the population lacks access to quality education, which has a direct impact on poverty levels.
Employment Opportunities
Without education, individuals are often confined to low-skilled, low-paying jobs, if they can find employment at all. The lack of education limits their ability to improve their living conditions and escape the cycle of poverty. In contrast, those with access to education are more likely to secure better-paying jobs, enjoy job security, and have the opportunity for career advancement.
Income Levels
Education is a key determinant of income. Studies have shown that each additional year of schooling can significantly increase an individual’s earning potential. In India, where economic disparities are pronounced, education can be the difference between living below the poverty line and achieving a stable, middle-class income.
Economic Growth
On a broader scale, the lack of education impedes India’s economic growth. A well-educated workforce is essential for innovation, productivity, and competitiveness on the global stage. By investing in education, India can harness its vast human capital to drive economic development and reduce poverty.
Barriers to Education in India
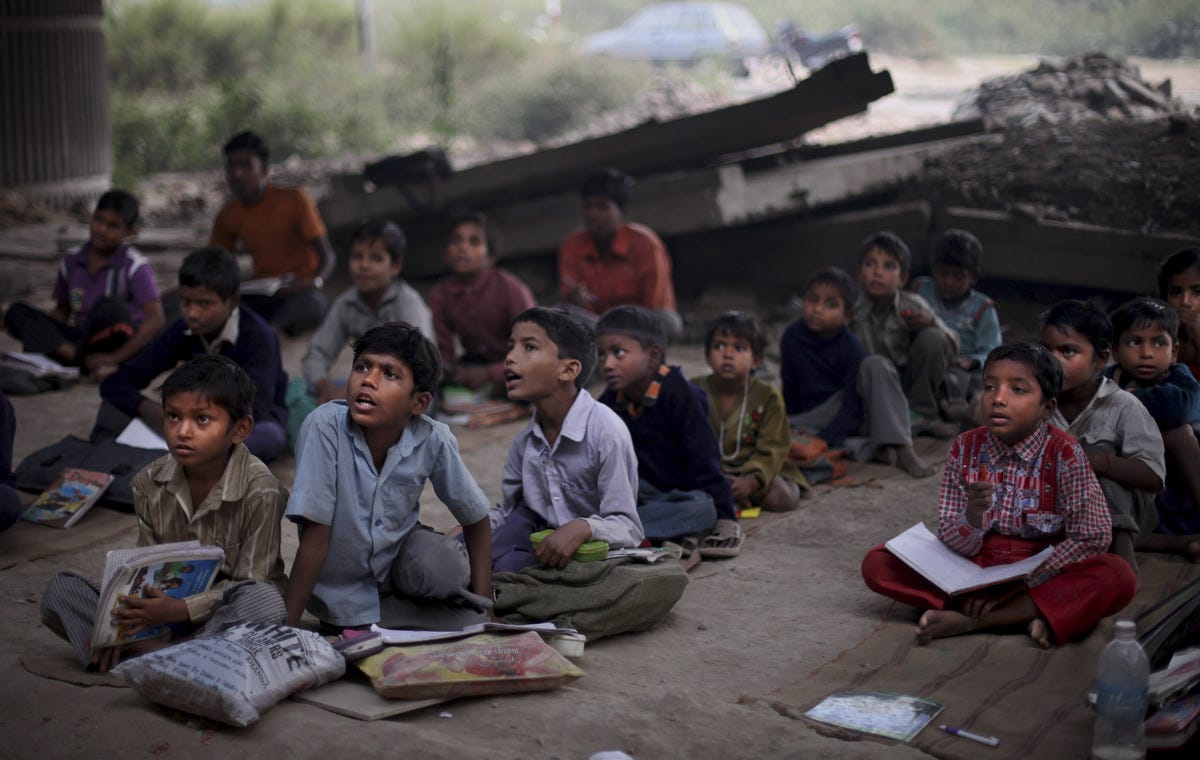

Several barriers prevent individuals from accessing education in India, including socio-economic factors, geographical challenges, and gender disparities.
Socio-economic Barriers
For many families living in poverty, the immediate need for children to work and contribute to the household income outweighs the long-term benefits of education. Additionally, the costs associated with schooling, such as fees, uniforms, and books, can be prohibitive for low-income families.
Geographical Barriers
India’s rural areas often lack adequate educational facilities. Schools may be too far for children to travel safely, or they may lack essential resources and qualified teachers. This geographical barrier significantly limits educational access for rural populations.
Gender Disparities
Gender discrimination continues to be a barrier to education for girls in many parts of India. Cultural norms and safety concerns can prevent girls from attending school, leading to higher dropout rates and limiting their opportunities for economic independence.
The Cycle of Poverty and Education
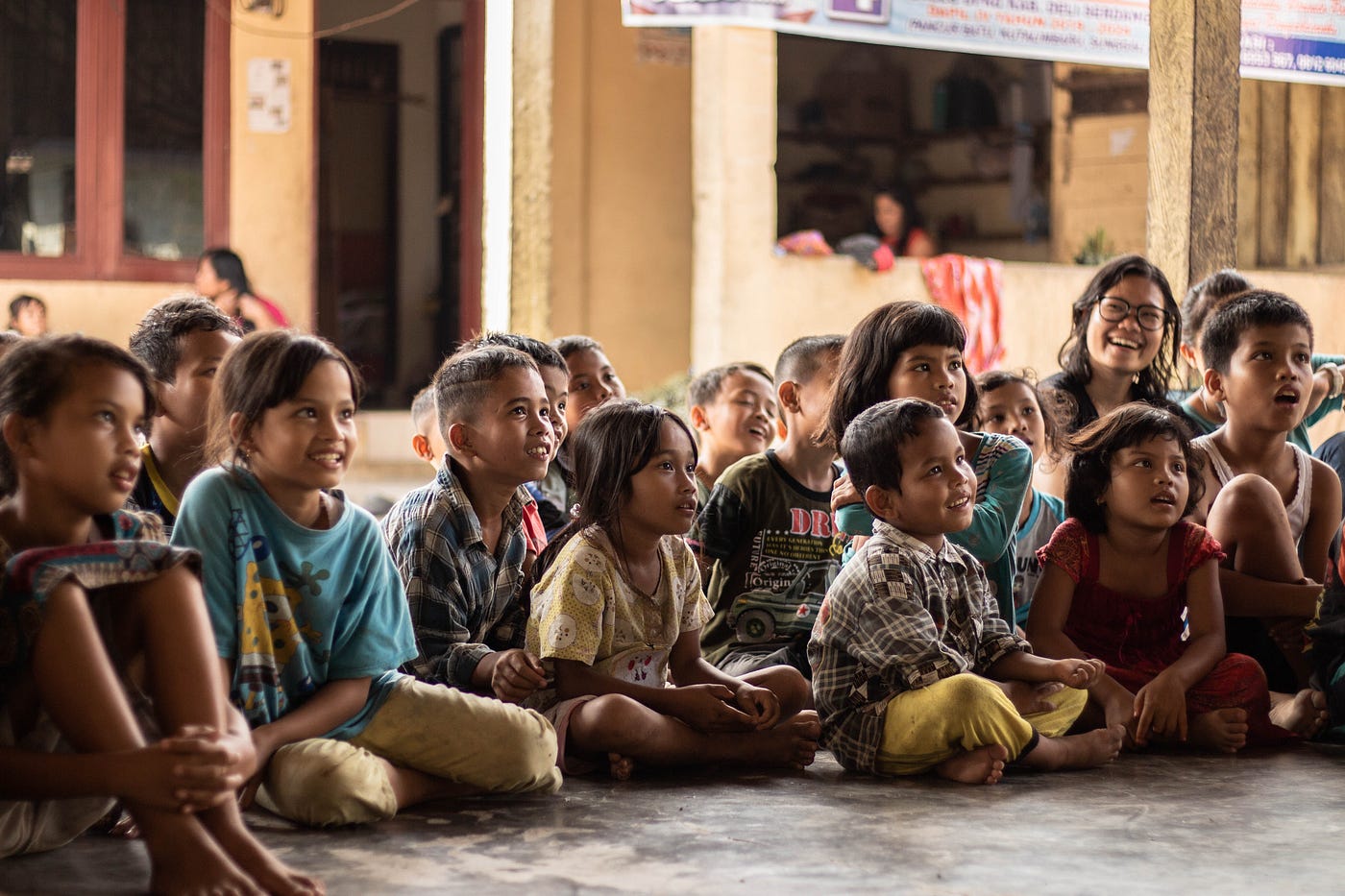

The relationship between poverty and education is cyclical: poverty limits access to education, and the lack of education perpetuates poverty. Families living in poverty often prioritize short-term survival over long-term benefits, such as education. This short-sightedness traps them in a cycle of poverty that can persist across generations.
Strategies for Improvement
To break the cycle of poverty through education, comprehensive strategies involving government, non-profit organizations, and community initiatives are necessary. Government policies must prioritize education, ensuring that schools are accessible, affordable, and of high quality. Non-profit organizations can play a crucial role in providing educational resources and support to underprivileged communities. Community-based solutions, such as local education programs and scholarships, can also make a significant impact.
Conclusion
The lack of education is a critical driver of poverty in India, limiting individuals’ employment opportunities, income levels, and the country’s economic growth. Overcoming the barriers to education requires a concerted effort from all sectors of society. By prioritizing education, India can empower its citizens, reduce poverty, and pave the way for a brighter, more equitable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is poverty?
Answer: Poverty is the lack of financial resources to meet basic needs like food, shelter, and healthcare.
2. What is human poverty?
Answer: Human poverty includes not only financial hardship but also the lack of access to education, healthcare, and essential services.
3. What are some common barriers to education that contribute to poverty?
Answer: Common barriers include high costs of education, social discrimination, geographical limitations, and poor quality of educational institutions.
4. How can vocational training help reduce poverty caused by the lack of education?
Answer: Vocational training provides practical skills that are directly applicable to the job market, enabling individuals to secure stable and well-paying jobs, thus reducing poverty.
5. What role do governments play in addressing the lack of education and poverty?
Answer: Governments can implement policies that ensure equitable access to quality education, provide financial support to students, invest in educational infrastructure, and create programs that address the needs of disadvantaged communities.









So true, education and poverty are deeply interconnected. Breaking the cycle starts with ensuring every child has the right to learn.