According to the Top boarding schools in India, education is an essential aspect of human development, and in India, it has been recognized as a crucial tool for socioeconomic progress. With over 1.3 billion people, India is one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing economies. Therefore, the Indian education system plays a significant role in shaping its future. In recent years, India has made notable progress in improving its education system, with a focus on increasing access, equity, and quality.
However, many challenges still need to be addressed to ensure that Indian education in India is accessible, inclusive, and effective. In this blog, we will discuss the latest trends in Indian education in 2023, exploring the current state of education in the country and the challenges that need to be addressed.
-
Technological Advancements in Education
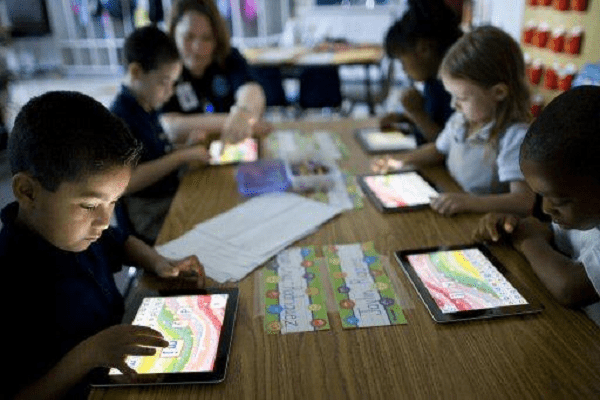

The use of technology in Indian classrooms has become a major trend in Indian education in recent years. With the increased use of smartphones and computers, schools have been able to incorporate interactive whiteboards, audio-visual tools, and tablets into their teaching methods to enhance student engagement and learning. Technology has also enabled teachers to create personalized learning experiences for each student, catering to their individual learning needs.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the emergence of virtual learning platforms, which have become the primary mode of education in many schools. This has given students and teachers the flexibility to attend classes from anywhere and at any time and has enabled students to access a wide range of educational resources, improving the quality of education. Despite its advantages, there are challenges to implementing technology in Indian education, including the digital divide and the need for teachers to be trained in using technology effectively. Click on the Best boarding schools in India to know more.
-
Emphasis on Skill-Based Education

In recent years, there has been a shift towards skill-based education in India, with a growing emphasis on developing practical skills in students. This has been a response to the demand for skilled professionals in various industries and the recognition that traditional Indian education systems are not always preparing students adequately for the workforce.
As a result, there has been an increasing incorporation of vocational training in school curricula. This includes programs in areas such as hospitality, healthcare, IT, and entrepreneurship, among others. The aim is to provide students with practical skills and knowledge that will make them more employable and better equipped for the workforce.
-
Diversity and Inclusivity in Education

Diversity and inclusivity have become increasingly important in education in India in response to past inequalities and discrimination based on factors such as caste, religion, gender, and socioeconomic status. To promote diversity, schools, and universities are taking measures such as reserving seats for disadvantaged students from Scheduled Castes and, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, and economically weaker sections. To reduce discrimination and prejudice, initiatives have been launched to promote social and cultural harmony among students, such as cultural festivals where students from different communities can participate and showcase their talents.
Steps have also been taken to provide education to marginalized communities, such as tribal communities, rural communities, and those living in slums. The government’s Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan program aims to provide elementary education to all children aged 6 to 14 years, and there are also NGOs working towards providing proper Indian education to children in slums and rural areas. While promoting diversity and inclusivity is a positive trend, there is still more work to be done to ensure that Indian education is accessible to all, regardless of their background or socio-economic status.
-
Environmental Education and Sustainability
Environmental education and sustainability have become important topics in the Indian education sector in recent years. India faces serious environmental challenges, and the government and educational institutions have recognized the need to promote environmental education and sustainability in schools and universities.
The government has taken steps to integrate environmental studies into school curricula, sensitizing students to environmental issues and encouraging them to take responsibility for environmental conservation. Schools and universities are also promoting sustainable practices, such as rainwater harvesting, solar energy, and waste management techniques, and offering initiatives such as eco-clubs, where students can participate in environmental conservation activities and projects.
It is crucial to educate students about climate change and environmental issues and equip them with the knowledge and skills necessary to mitigate these impacts. This education is critical in developing a sustainable and responsible approach to the environment, and ensuring that students understand the implications of their actions on the environment. The emphasis on environmental education and sustainability in the Indian education sector is an important step towards creating a more environmentally conscious and responsible society.
-
Rise of Alternative Education Models

In recent years, alternative education models such as homeschooling and online education have gained popularity in India. These models have had a significant impact on the traditional Indian education system and forced institutions to adapt to the changing times by incorporating technology into their curricula.
While homeschooling provides parents with greater control over their child’s education and online education offers more flexibility in terms of time and location, both models have their drawbacks. Homeschooling may not provide children with the social interaction and diversity offered by traditional schools, and online education may not be suitable for all learners.
Despite these potential drawbacks, alternative education models are likely to continue to gain popularity in India and play a more significant role in the Indian education system in the future. This shift towards alternative education models is a reflection of changing attitudes towards traditional education and a desire for greater flexibility and control over the learning process.
-
Government Policies and Reforms
The government of India has implemented various policies and reforms to improve the quality of education in the country. The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA) are two significant policies that aim to transform the Indian education system.
The NEP emphasizes skill-based education, promotes multilingualism, and integrates technology in Indian education, while the SSA aims to provide universal access to quality education and improve the infrastructure of schools. The introduction of new policies and reforms, such as a new curriculum for primary and secondary schools focusing on critical thinking and problem-solving skills and the establishment of new universities and colleges in underserved areas, will increase access to higher education for students in those regions.
The success of these policies and reforms depends on their effective implementation, with adequate resources allocated to support them. Additionally, the involvement of all stakeholders, including teachers, students, parents, and the community, is crucial for their success. The government’s policies and reforms have the potential to transform the Indian education system in India and provide students with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the 21st century, but their success ultimately depends on proper implementation and support from all stakeholders.






